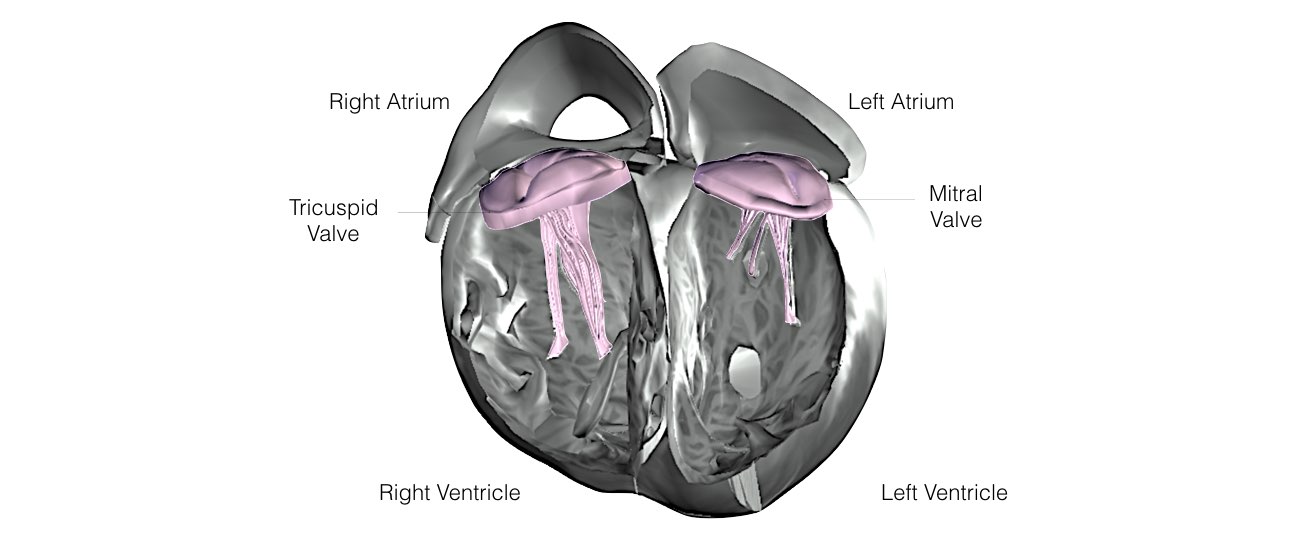
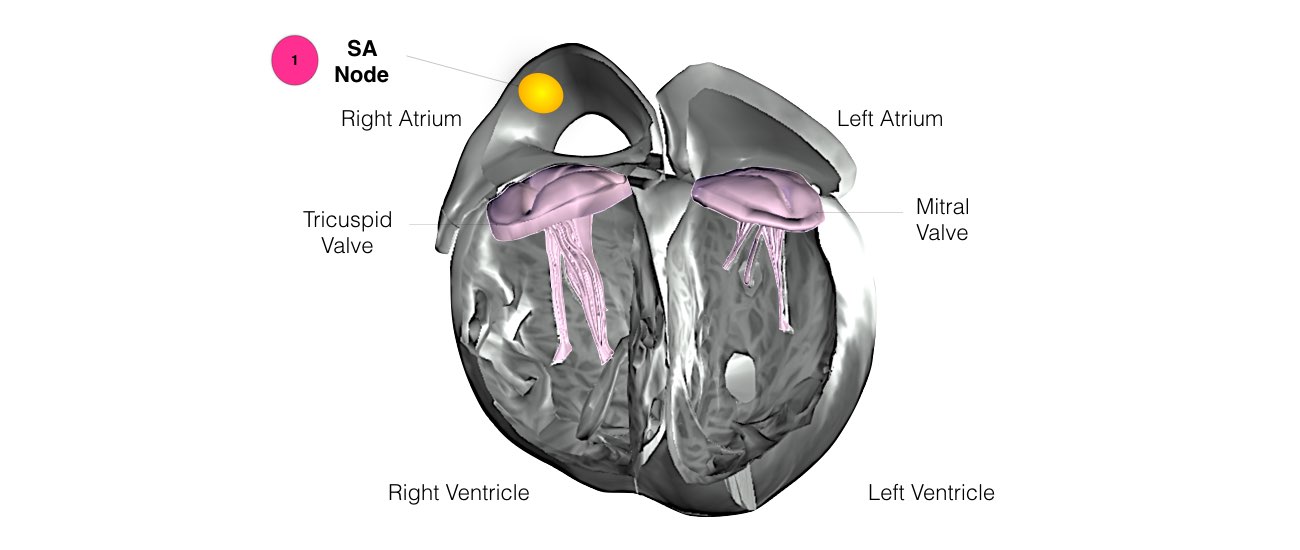
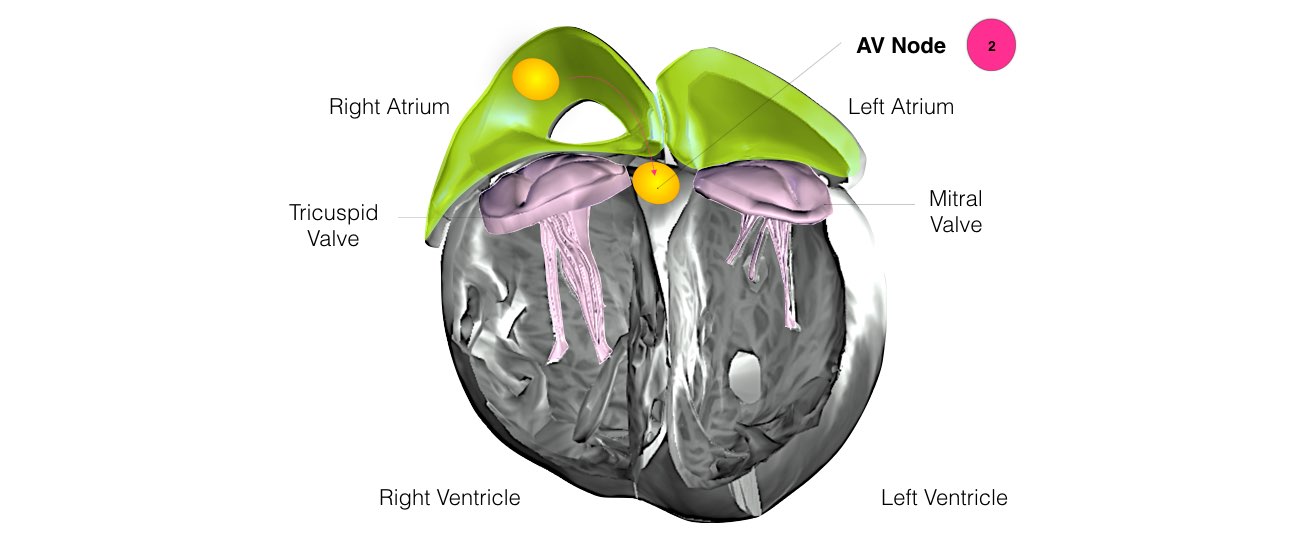
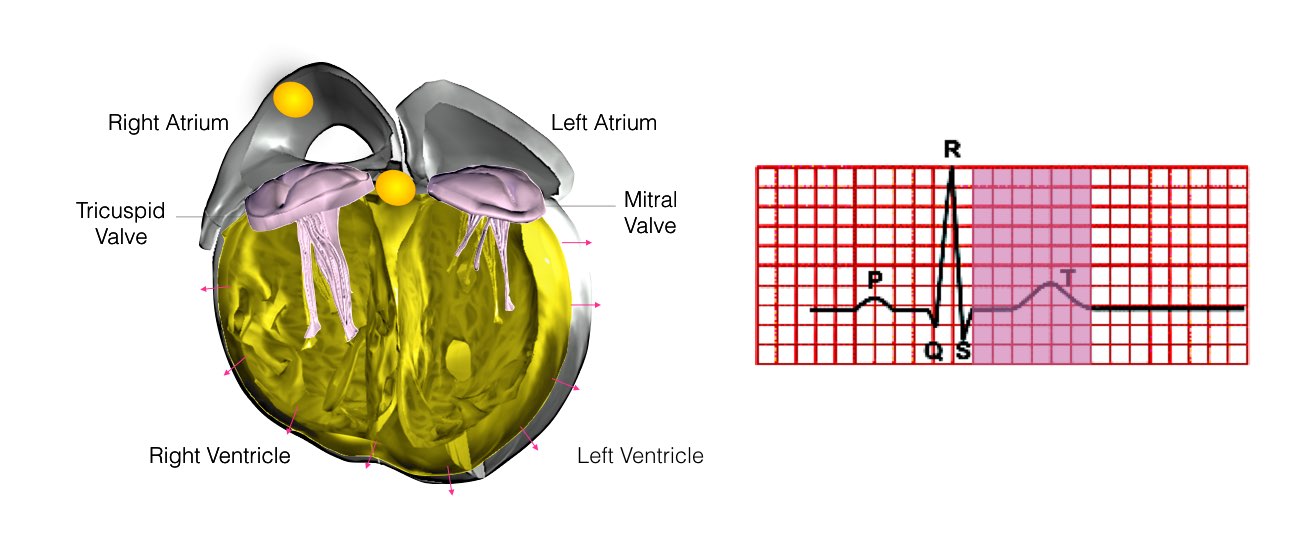
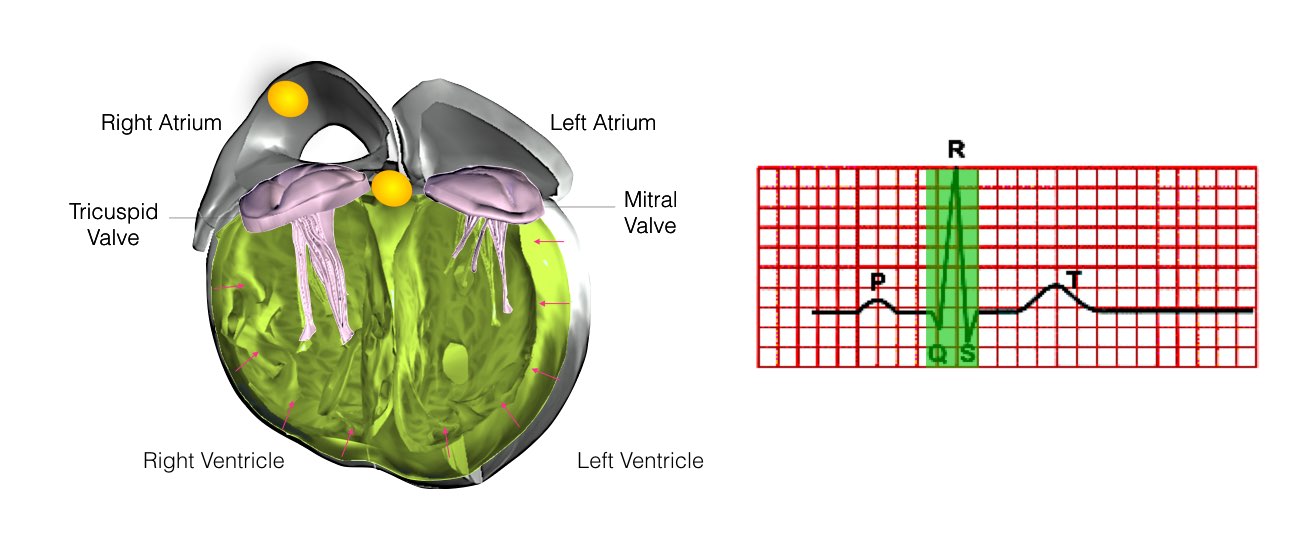
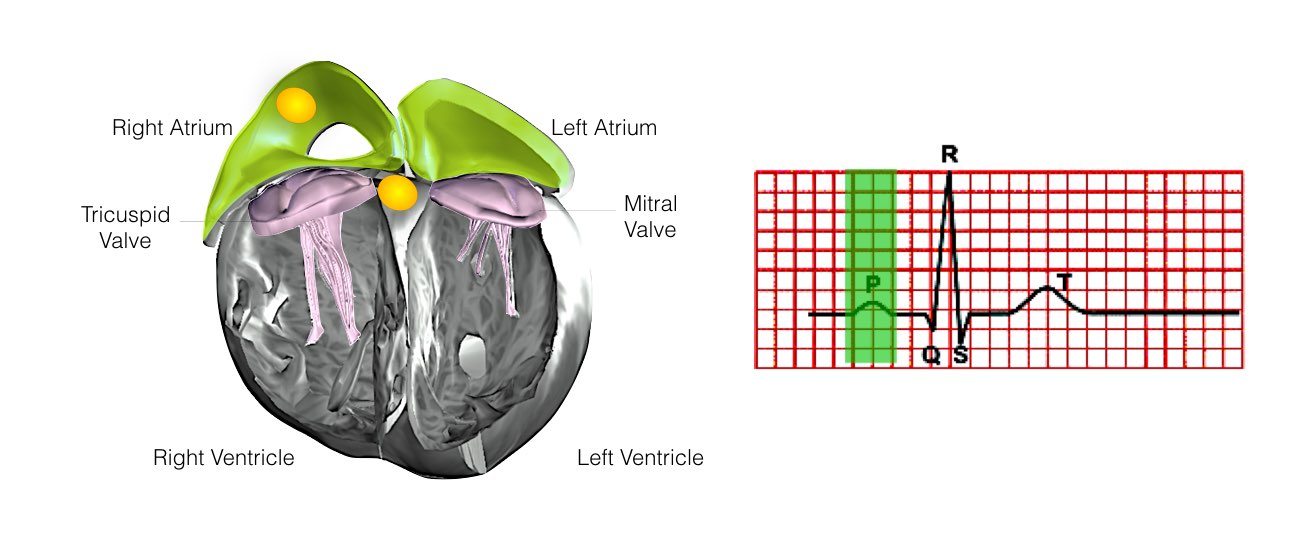
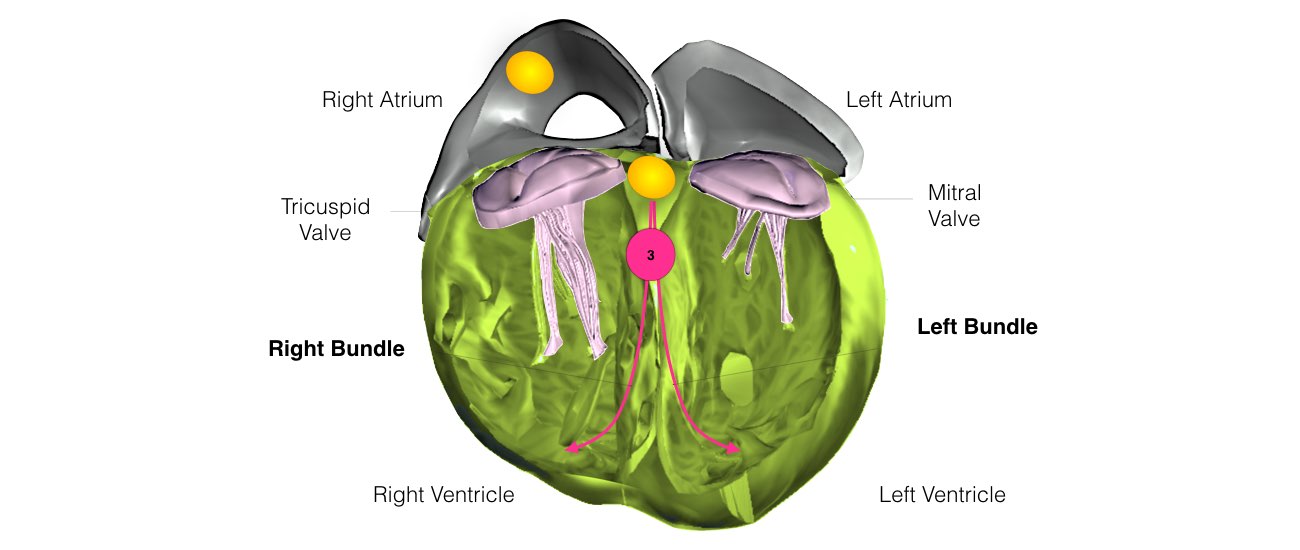
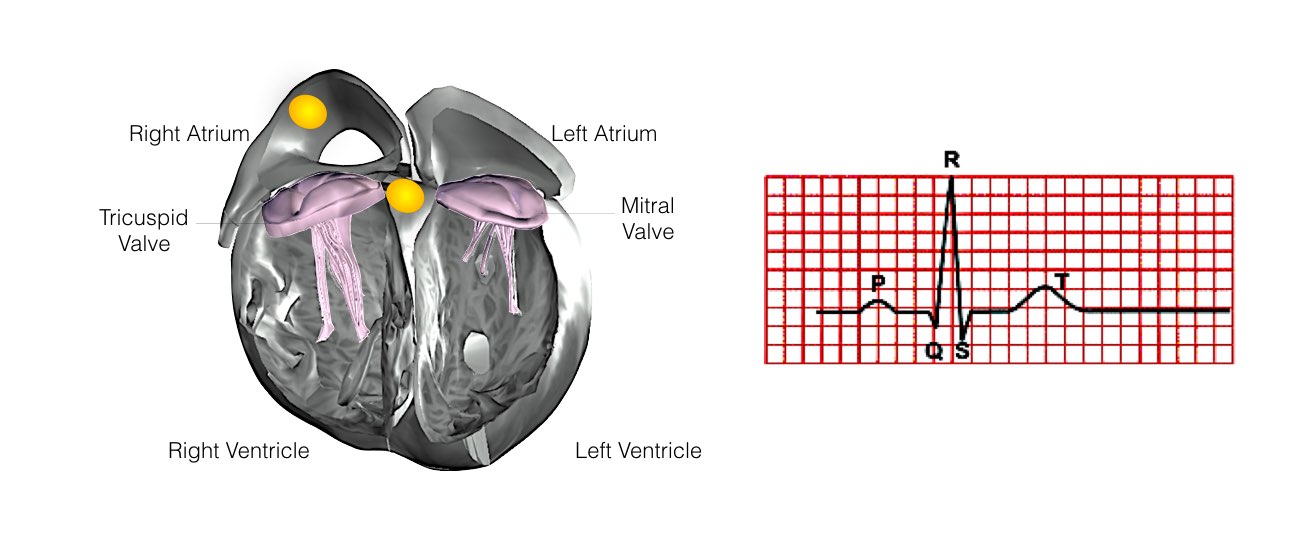
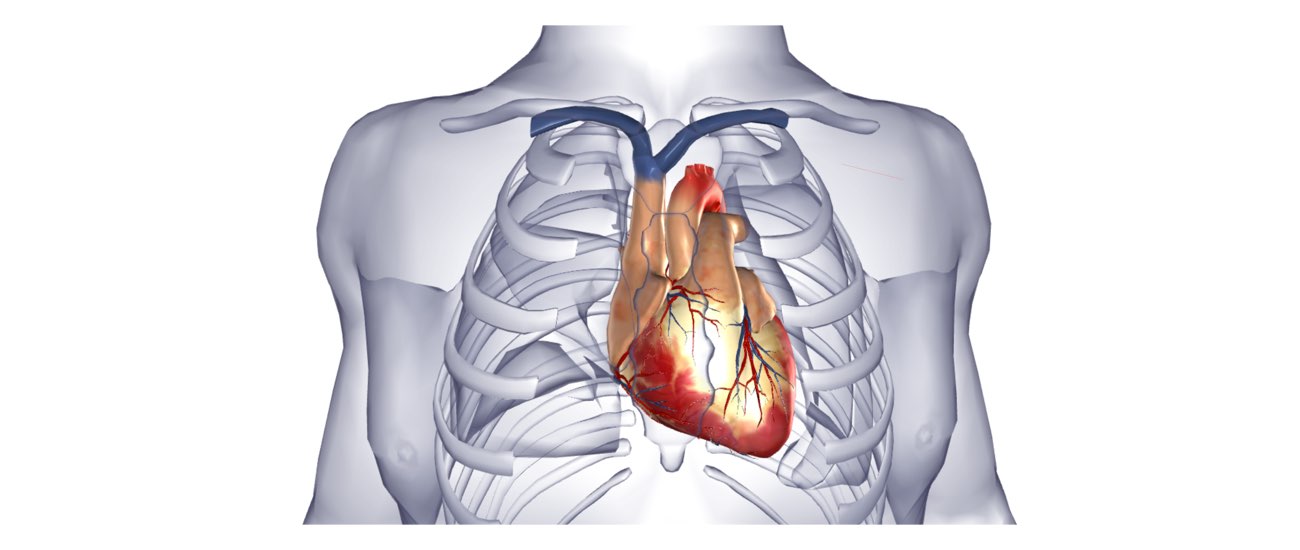
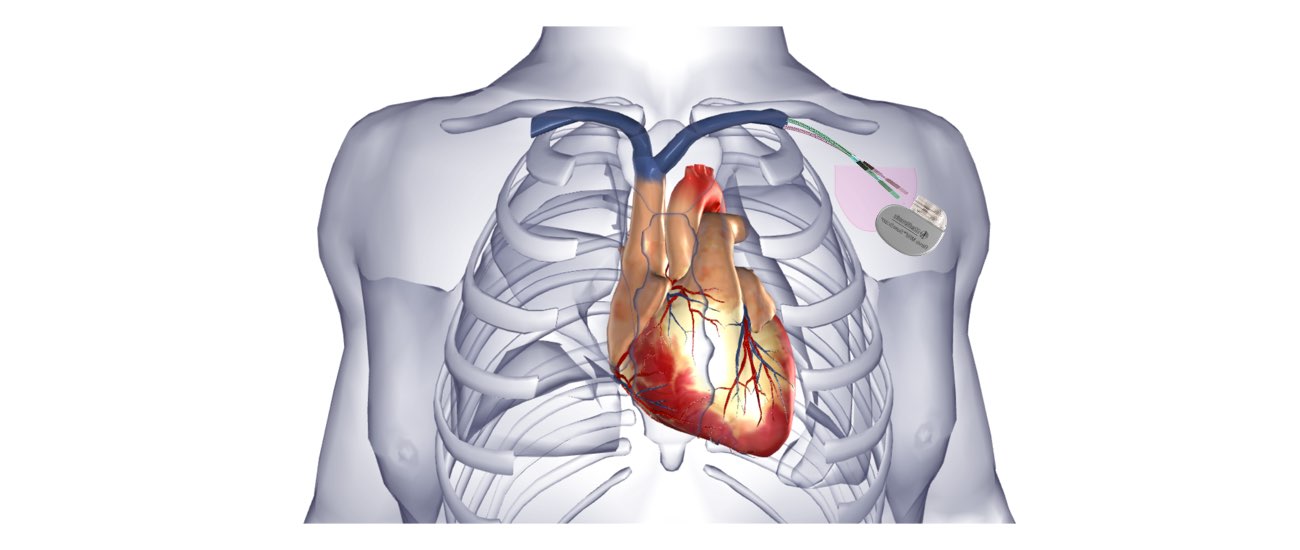
The heart is a pump responsible for maintaining the blood supply to the body. It has four chambers. The two upper chambers (the right atrium and the left atrium) are the chambers that receive blood as it returns from the body via the veins. The lower chambers (the right and left ventricles) are the chambers responsible for pumping the blood out to the body via the arteries. Like any pump, the heart has an electrical system that controls how it functions.
Menu
- Home
- About
- Learn
- Normal Heart Function
- Supraventricular Tachycardia (SVT)
- Ectopics / Missed Beats
- Bradycardia (Low Pulse Rate)
- Syncope
- Atrial Flutter
- Atrial Fibrillation
- Long QT Syndrome
- Brugada Syndrome
- Heart Failure
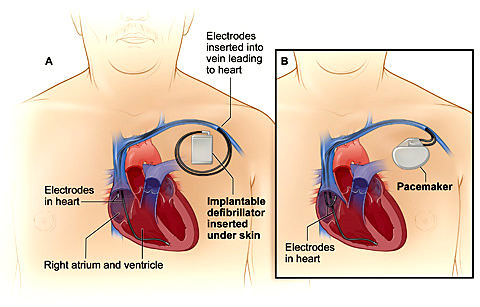
- Pacemaker
- Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator (ICD)
- Ventricular Tachycardia in Normal Hearts (Idiopathic-VT)
- Coronary Artery Disease
- Ventricular Tachycardia in Structural Hearts Disease
- Services
- FAQs
- Media
- Contact
- Blog
close
Menu
- Diagnostic Tests
- Heart Rhythm Procedures
- Heart Rhythm Procedures
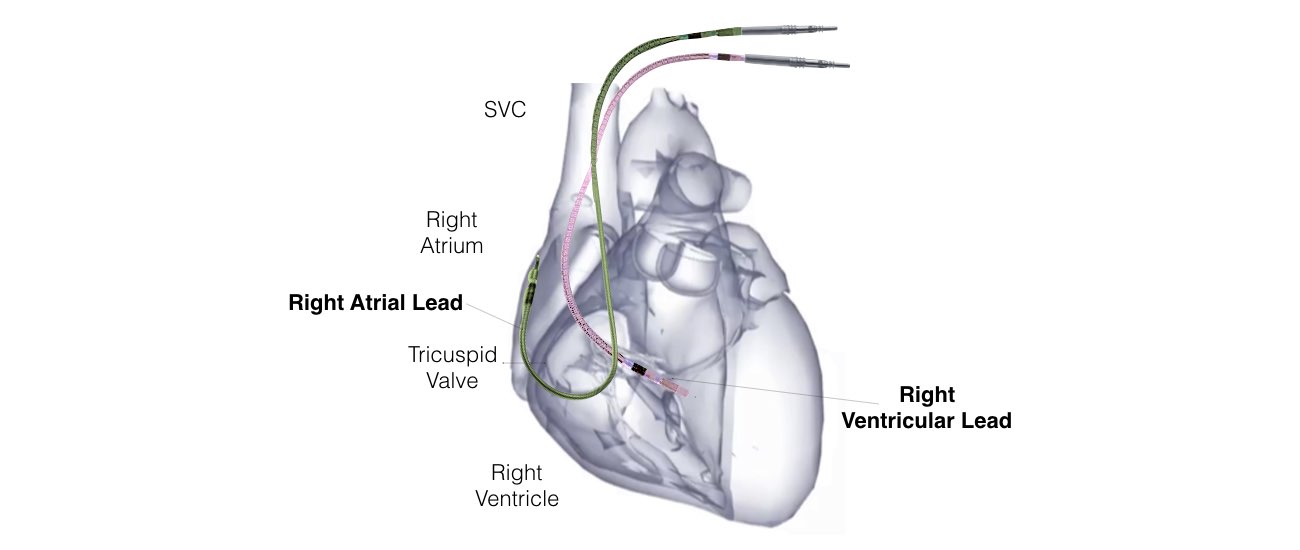
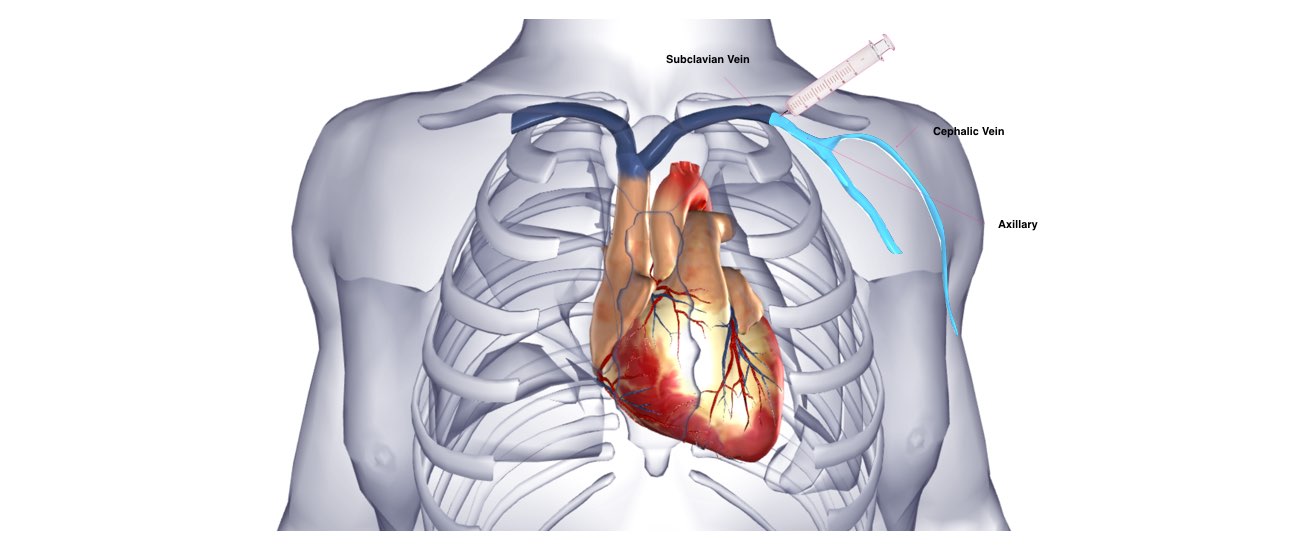
- Permanent pacemaker implantation
- Physiological Pacing
- Pediatric Pacemaker Implantation
- Leadless Pacemaker Implantation
- AV Node Ablation Plus Pacemaker Implantation
- Automatic Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator (AICD) Implantation
- Cardiac Resynchronisation Therapy (CRT)
- Pacemaker and Defibrillator Extraction & Revision
- Implantable Loop Recorder (ILR)
- Coronary & Structural Cardiac Procedures
close